Data Source Basics
Ultorg works with data in tabular formats, stored in external data sources. These include SQL databases such as PostgreSQL or MySQL, cloud-hosted Google Sheets spreadsheets, and local CSV or Excel files. Ultorg itself runs on your own computer, which keeps your data private.
Adding a Data Source
To add a data source, click the Add Data Source button in the Folders sidebar, and select the type of data source to add. Then follow instructions specific to your data source type, found in the other pages in this chapter.

In the sidebar, a data source icon () will appear with data tables (
) underneath. Double-click any data table to open a new perspective based on that table. A perspective is Ultorg's visual equivalent of a SQL query. The simplest kind of perspective, which you get when you double-click a data table, just shows the contents of the table:

Some data sources may group tables into different schema folders (). You can also group tables in folders yourself, by right-clicking the data source and clicking New Folder, and then dragging the desired tables into the folder. Folders that you create yourself are shown with a plain folder icon (
), and do not affect the external data source.
Data tables that represent a VIEW or MATERIALIZED VIEW in a SQL database have a subtle “v” indication on their data table icon (). They otherwise behave the same as other data tables.
Perspectives and Data Sources
As will be shown in the Building Perspectives chapter, a perspective can pull data from any number of data tables. The data tables can be from a single data source, or from a mix of data sources. In the following example, the open perspective pulls data from three tables, Courses, Readings, and Meetings, in the Course Catalog data source:

In the Folders sidebar, a blue arrow () indicates which table, and which data source, the data in the currently selected perspective cell is coming from.
Query Execution
As you interact with a perspective, Ultorg generates SQL queries that can run directly on your data source. For data sources that do not provide their own SQL engine, or when your perspective combines tables from multiple data sources, Ultorg executes queries on your local computer instead. You can also force local execution with a setting. See Local Query Execution.
Ultorg's SQL generator has dedicated support for the SQL dialects of PostgreSQL, MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, DuckDB, and BigQuery, and is regularly tested with each of these databases.
Changing Settings
You can edit the connection settings of a previously created data source, e.g. to change the host name of a database or the path to a file. To edit a data source, right-click the data source () and click Edit Connection Details:

You can hover the mouse over a data source to show a summary of connection details:

Besides the data source specific connection details, there is an Other Data Source Options action with additional options. See Auto-Format Field Names and Local Query Execution.
Replacing a Data Source
If you edit the connection details of a data source, the changes will affect all perspectives that reference said data source. In some cases it may be more practical to keep multiple data sources available, and switch between them at the perspective level. For example, you may switch between production and development environments.
The Data→Replace Data Source action changes the data source that is referenced by the current perspective, without otherwise modifying the query:
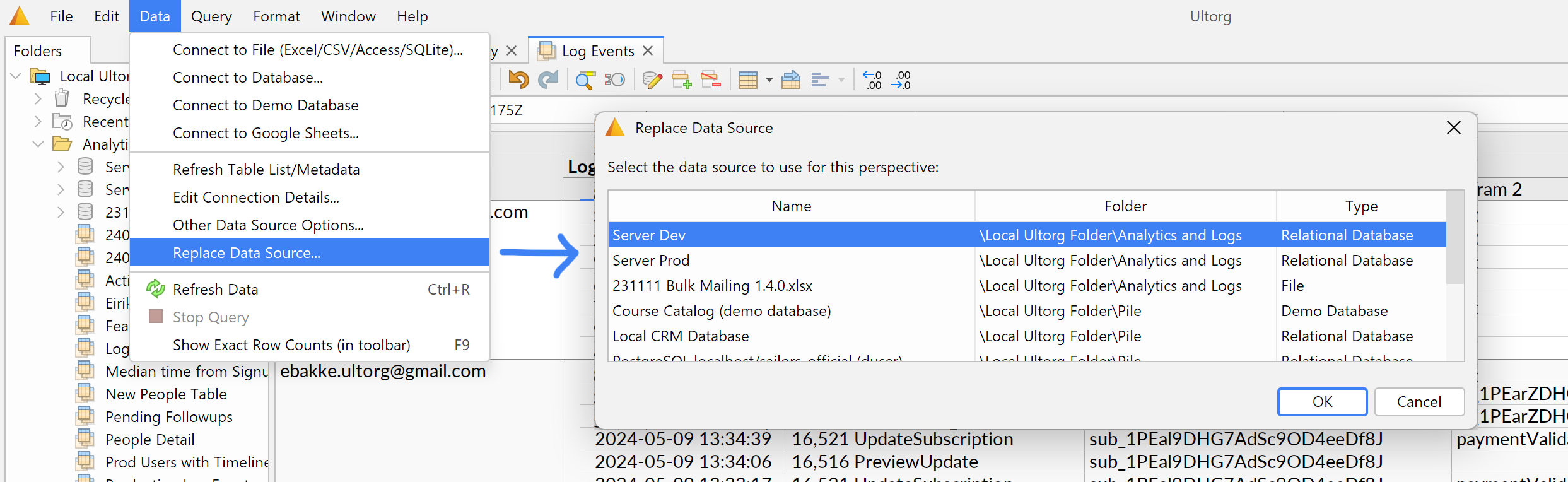
For perspectives that include tables from multiple data sources, the cursor position is used to determine which data source should be replaced.
This action is primarily useful when the old and new data sources are of the same type and contain tables and columns with identical names. Further options may be added in future Ultorg versions.
Deleting a Data Source
You can delete a data source by selecting it in the Folders sidebar and pressing the Delete key. The data source will be moved to the Recycle Bin (). If there are saved perspectives still referencing the data source, an error message will be shown:
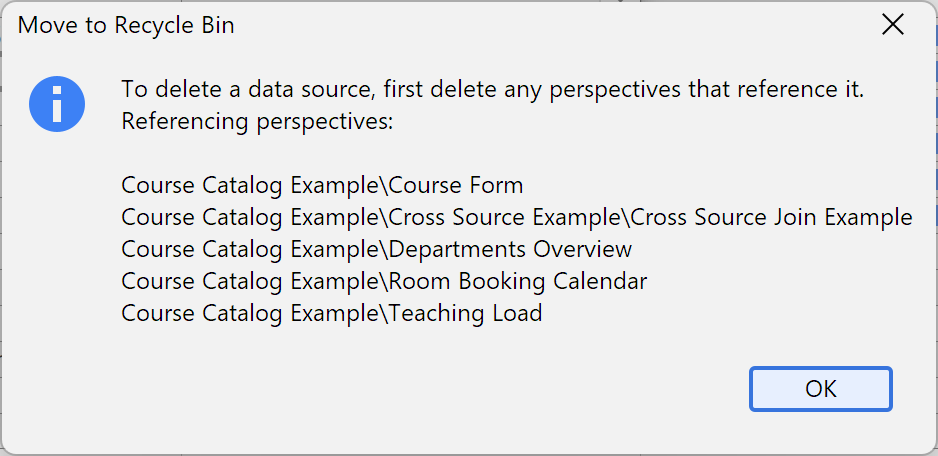
Other Actions
Refresh Metadata
If the list of tables or table columns has changed in the external data source, you can right-click the data source in the Folders sidebar and click Refresh Table List/Metadata to make Ultorg see the changes. This also disconnects and reconnects any underlying network connection.
In existing perspectives, newly appeared table columns are shown with a small plus sign on their field selector icon ().
Disconnect
Relational database connections are automatically disconnected after 15 minutes of inactivity. An explicit Disconnect action also appears when you right-click the connection.

Manual disconnection is useful primarily when external software depends on it, e.g. if a maintenance script or SSH command is waiting for the connection to close. Or, you can disconnect to reset “stuck” network connections, instead of waiting for a timeout.
Each data source has at most one network connection open at a time.
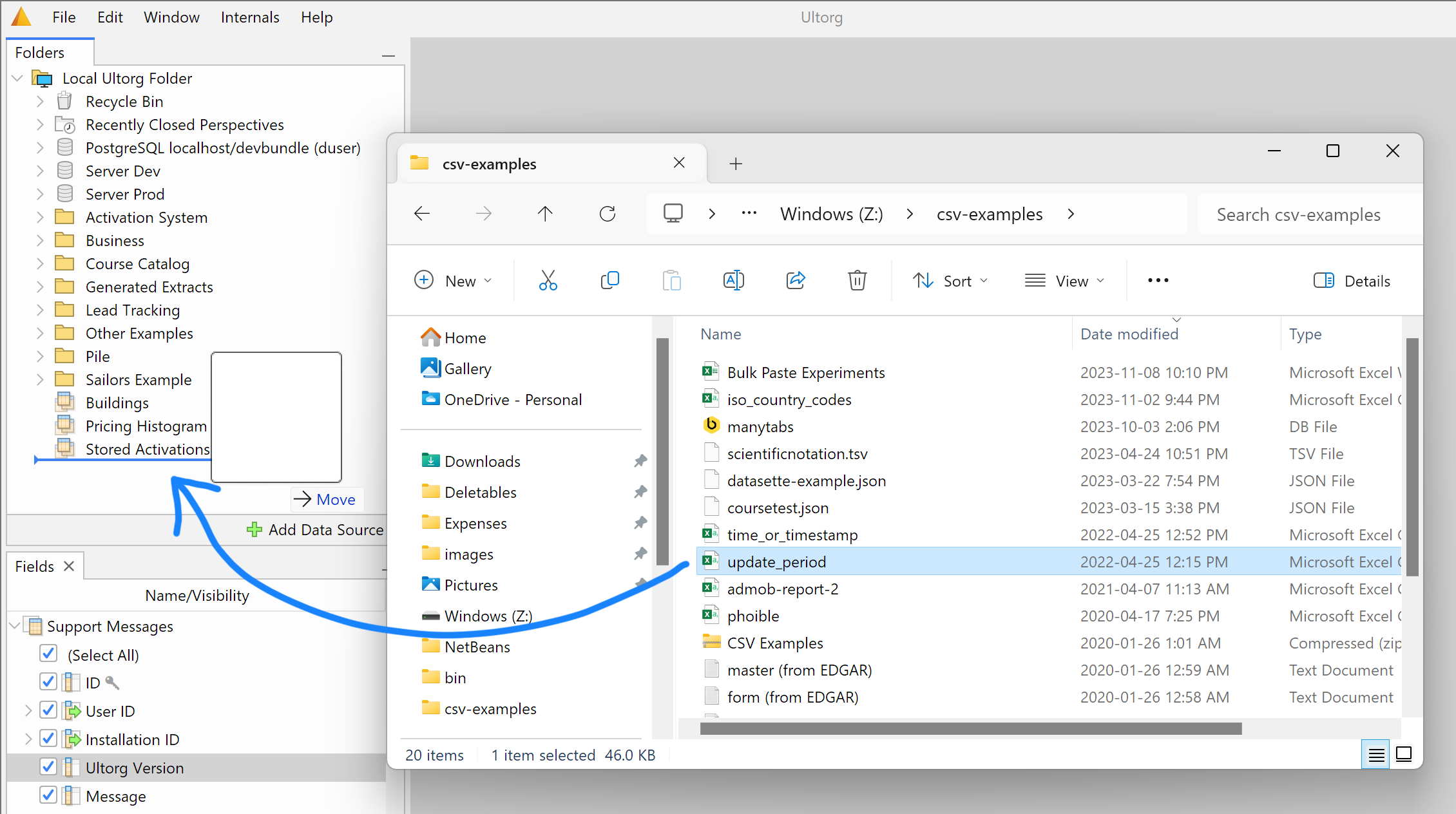
Browse or Drag File
To add a file-based data source, such as a CSV file or Excel file, click Add Data Source→Connect to File, and browse to the file.
Alternatively, you can drag one or more files from the your operating system's file explorer to the Folders sidebar in Ultorg:
UNION of Multiple Tables
In some datasets, a single large table is split into smaller individual tables, with similar column names and data types. For example, a historical dataset spanning multiple years might be delivered as one CSV file per year. In this case, it may be useful to combine the data back into a single table in Ultorg before doing further work on it. This can be done as follows:

- In the Folders sidebar, select all of the data tables (
) to combine. To select multiple items at once, hold down the Ctrl key (Command key on Mac) while clicking each table.
- Right-click the selection and click Create Extract(s).
- In the dialog box that appears, click Combined Extract.
A new extract table () will appear, which you can double-click to open in a perspective.
For more information, see UNIONed Data Extracts. If you need to stack tables horizontally rather than vertically, i.e. using a join rather than a UNION, see Multi-Source Queries instead.